DVB-S2X is an extension of the established satellite communication standard DVB-S2 and exploits the full potential of satellite communication. It improves the performance and spectral efficiency of the transmission and thus enables more data throughput with the same bandwidth. DVB-S2X also offers additional features for more robust communication or new applications and flexible usage scenarios.
DVB-S2X Technology
DVB-S2X features
A plurality of the technical improvements in DVB-S2X is focused on improving performance and spectral efficiency, both in the physical layer (PHY) and on system level:
| IMPROVEMENTS | BENEFITS AND APPLICATIONS |
| Increased granularity in modulation and coding (MODCODs) | Better utilization of the transmission channel for broadband applications |
| Pulse shaping with sharper roll-off filters | Provides capacity gains for most applications through better utilization of the available spectrum |
| Higher modulation schemes: up to 256APSK | Extended data rate range is beneficial for broadband applications on modern high-throughput satellites (HTS) and for professional equipment using high gain ground antennas |
| MODCODs optimized for linear transponder | Typical use case for the return link in broadband or for remote site or backhaul connectivity on bandwidth-lease transponders |
| Support for ultra-wideband carrier | Allows the entire transponder bandwidth to be used by a single carrier in broadband applications |
| Channel bonding | Feature to increase efficiency at system level by bundling bandwidth distributed across several transponders into one logical channel |
| Co-channel interference mitigation | Higher data throughput with HTS satellites |
| Improved multiplexing gain | Reduces the overhead reserved for temporal peak capacity demands on wideband carrier and on channel bonded transponders |
Besides performance improvements, DVB-S2X also adds a number of physical layer and system level features for new use cases or for improving the robustness in existing applications, including very low signal-to-noise ratio (VL-SNR) operation and a new efficient super-frame structure. Super-framing allows for new transmission techniques like precoding and beam hopping.
Finding the right feature set and implementing it
We at Fraunhofer IIS were actively involved in the development, specification and validation of DVB-S2X. Based on this experience, we develop customized solutions for DVB-S2X-based receivers and systems. The large number of features and the many possible target applications and services pose a few challenges when implementing the DVB-S2X standard. Depending on the application, there are normative, optional, but also non-applicable features. In this context, DVB-S2X should be seen as a toolbox with certain tools addressing certain challenges and opportunities. When implementing DVB-S2X, it is important to decide which tools are suitable for the planned application and the market being addressed.
Implementing DVB-S2X is further complicated by the throughput range a receiver may have to cover. In some cases, the required receiver resources grow disproportionately with carrier bandwidth and throughput. It is therefore not only a question of the supported feature set, but also about the trade-off between throughput and complexity of the implementation.
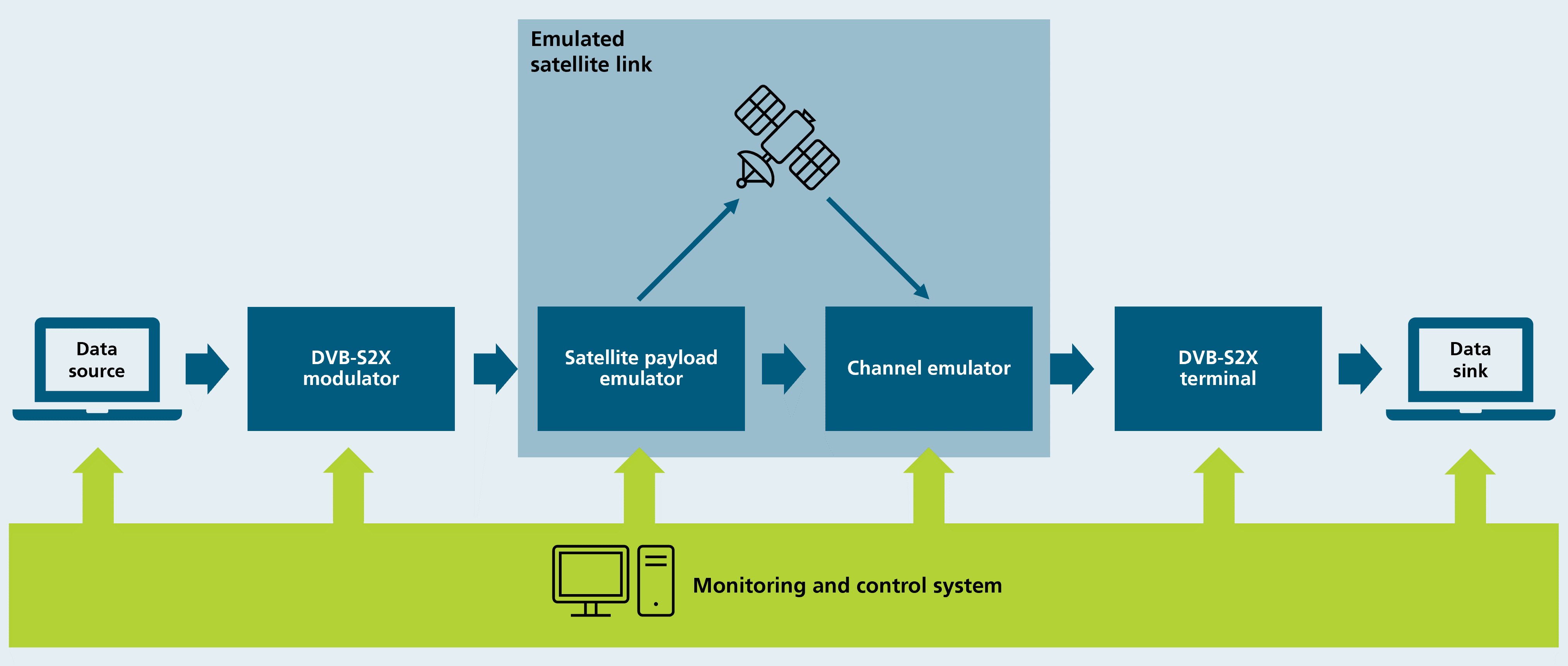
DVB-S2X test bed
Our DVB-S2X test bed considers the entire transmission chain: Transmission takes place from the data source to the transmitter (modulator) and then via an emulated satellite link to a receiver terminal. There, the signals are demodulated, decoded and then forwarded to a PC for evaluation. The test bed has a comprehensive monitoring and control system for testing the function and performance of radio interfaces and transmission methods. To carry out such tests, we use our own specially developed DVB-S2X receiver implementation that enables direct switching between three different operating modes.
Functions of the DVB-S2X test bed
- Detailed analyses of the functionality and performance of radio interfaces and transmission methods
- Testing of DVB-S2X devices and proof of compatibility with the DVB-S2X Annex-E super-framing specification
- Configurable transmission scenarios (e.g. overflight of a LEO satellite) and automated measurements of performance values
- Flexible multiplexing of different data streams and formats, e.g., internet protocol (IP) or transport stream (TS)
- Feedback procedures for automatic optimization of the transmission performance such as predistortion or adaptive coding and modulation (ACM)
- Switching between normal continuous wideband transmission and beam hopping transmission (based on super-frame format 4 and 5)
Performance values and features of the DVB-S2X test bed
- End-to-end transmission in the L-band with maximum speeds of up to 1.5 Gbit/s
- Symbol rates of up to 400 MBaud, respectively bandwidths of up to 500 MHz for broadband transponders
- Supports transmission scenarios with very low signal-to-noise ratio down to -10 dB (VL-SNR)
- Supports over 250 logical channels with individual quality of service (QoS)
- Supports DVB-S2X-specific functions such as variable coding and modulation (VCM), adaptive coding and modulation (ACM), time slicing, all specified APSK modulations and roll-off factors as well as forward error correction using LDPC/BCH