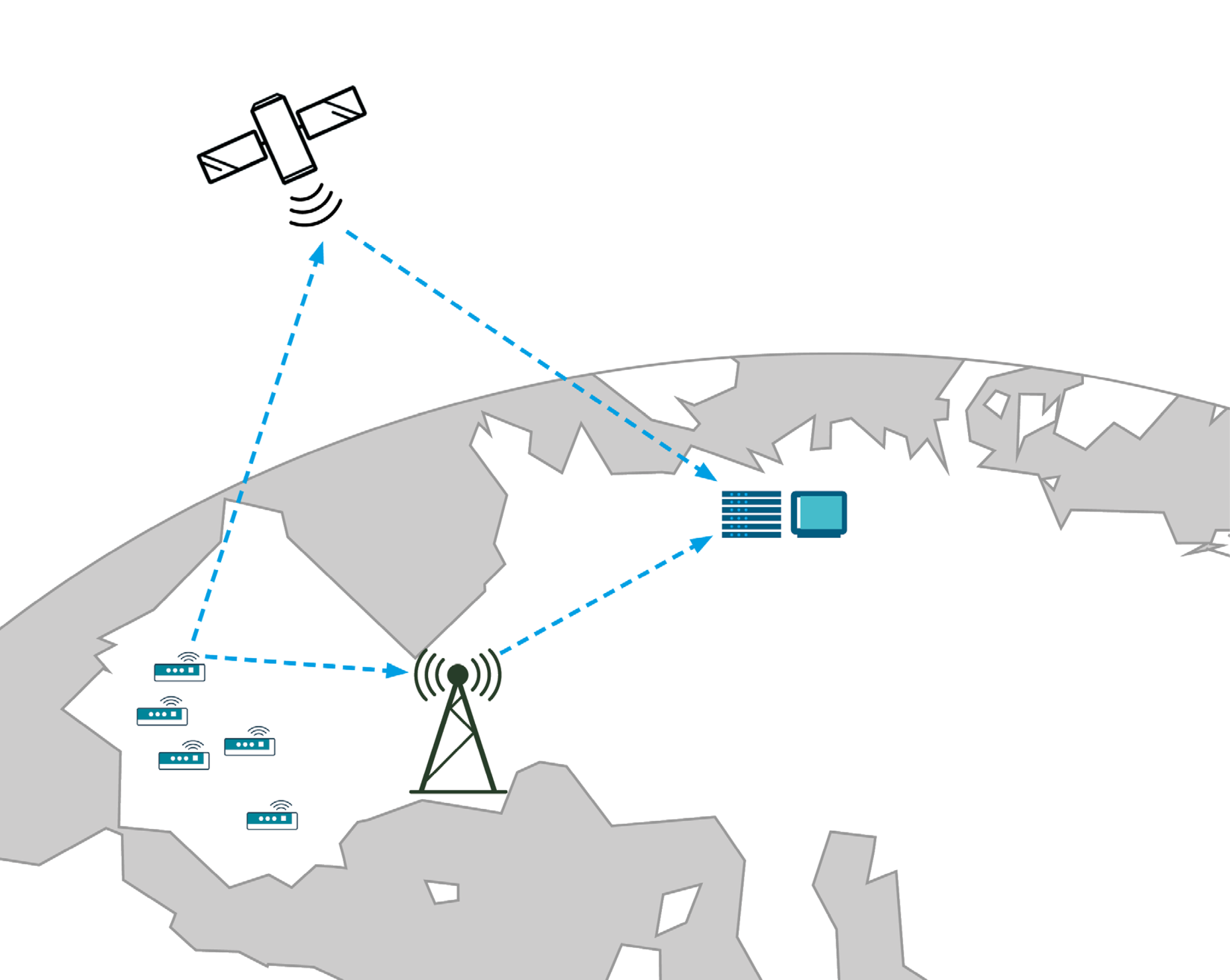
Wireless data transmission systems are being increasingly deployed in industrial and home automation applications. These robust systems are used to transmit sensor data and control information across network infrastructures. In the age of the Internet of Things (IoT), people and things will be intelligently connected to one another, leading to innovations in business and Industry 4.0.
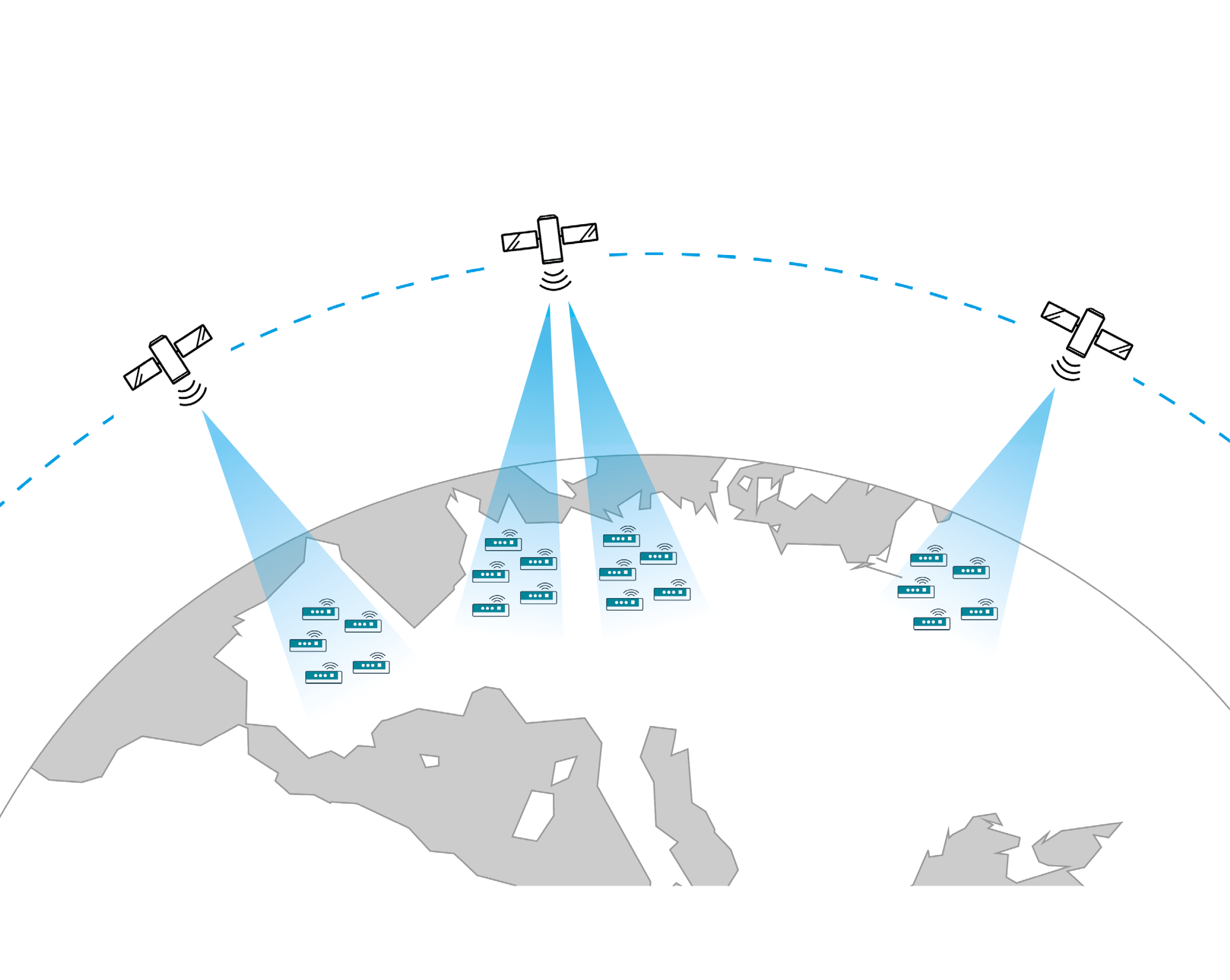
While the majority of IoT networks is terrestrial, IoT applications also provide various opportunities for established and newfound satellite operators, especially in connecting remote areas that lack terrestrial infrastructure. Opportunities range from selling additional capacity on GEO (geostationary) satellites in C-, Ku- and Ka-band for direct or backhaul connectivity to deploying new LEO (low earth orbit) or HEO (highly elliptical orbit) constellations, optimized for the IoT market.
Our solutions and IP (intellectual property) address many of the technical challenges in IoT communication, both terrestrially and via satellite.