Solution
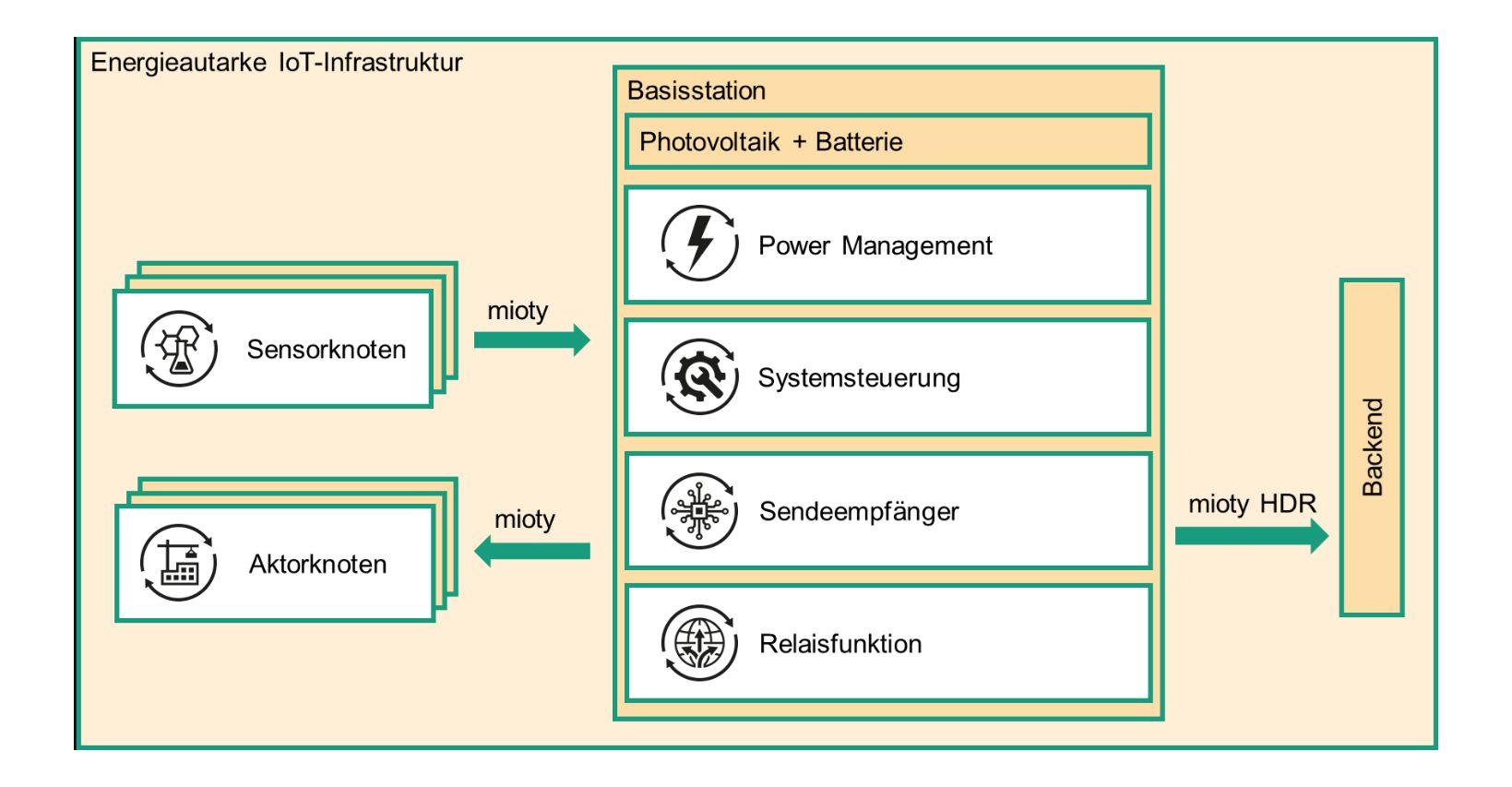
The "Energy-autonomous IoT infrastructure" (EIOTI) project is addressing this problem. As part of the project, an energy-optimized LPWAN base station is to be developed that is used for wireless sensor networks. Energy is to be supplied entirely via energy harvesting using energy sources from the direct environment, such as movement or light.
For this purpose, a transmission functionality including an adapted waveform for the base station is to be developed, through which a base station can act as a relay: It then sends the received sensor data on to the next supplied infrastructure point. In addition, an energy supply module is to be developed that primarily uses small solar modules to supply the base station or to store the energy generated in a battery in the medium term. Wind and water turbines are also an option for the module.
The LPWAN technology mioty® is used for data transmission in the project. Compared to other wireless protocols, mioty® requires only a fraction of the energy to transmit the same amount of data in the previous standard profile. In addition, mioty® is highly scalable, which is important for the interference-free coverage of additional use cases. mioty® supports up to 24 times as many connections compared to existing LPWAN technologies.
To ensure that the base station is not only energy self-sufficient but can also run in the absence of (mobile) infrastructure, a new type of high data rate profile (HDR) is to be developed and implemented for mioty® during the course of the project in order to forward the received sensor data to the backend.